Lucarnes in the attics of private houses. Dormer windows three ways of installation Lucar windows
Dormer windows, regardless of type, are attached to rafter system buildings, and hatches also have a rafter frame. Flat windows built into the roof are also called dormer windows. But windows are built only into the rafter structure, and not into the window frames. A roof window can have a frame made of wooden block, plastic or metal-plastic. Lightweight roof window structures are installed using lower horizontal beams attached to the rafter system.
Installation and installation of roof windows
When installing roof windows, it is important to maintain horizontal and vertical installation. The first step is to level the lower half of the attic window using a building level, then secure it in the corners with self-tapping screws. The second stage of installation is to align the length of the window and check the parallel relative to the rafters, then preliminary fastenings are made in the corners of the window using self-tapping screws that are not fully screwed in to allow for subsequent straightening. The final fastening is carried out only after full verification of all dimensions and accuracy of orientation of the entire window structure. The attic window will maintain a stable position if the frame is precisely aligned with the rafters - the distances should be equal, such alignment will allow the structure to be firmly held after complete fastening. The last stage Once again check the accuracy of installation vertically and horizontally and screw in the screws completely.
For roof windows, high-quality waterproofing, strong and reliable, is very important, since the window is a structural part of the roof and takes on the same atmospheric influences as the roof of the house - snow, rain, wind, etc. Insulating materials are laid in a special way - only from the lower levels to the upper ones, for the most precise fit to window frame. Overlaps and excess waterproofing material are not needed, and all joints with insulation require additional fixation with self-tapping screws.
When installing a roof window in a roof made of corrugated sheets, special profiled or corrugated slats with attachments are used that fit precisely with the profiles of the roof deck. These attachments are installed at the bottom of the frame and have side projections.
Double-glazed windows or sash roof windows are installed in the frame after waterproofing has been installed. Insulation of attic windows is carried out with inside, from the premises. Insulating materials are laid completely over the entire area of the frame, top layer serve foil thermal insulation materials. The fastening is carried out using self-tapping screws and must be airtight and not create cold bridges; there is a special fastener for this.

Preparing to install roof windows
Before installing roof windows in the attic structure, you should familiarize yourself with their types and the capabilities of certain models. The main requirement for structures is strength and reliability, as well as complete tightness in closed– the window should not allow rainwater and moisture to pass through.
The possibilities of attics are enormous - these are additional rooms that house not only bedrooms or dressing rooms, but also kitchens and even sanitary facilities. Provide street lighting, in winter - windows help heat from the sun's rays. Cozy and practical attic rooms usually become favorite places to relax for all residents of the house, because special atmosphere Attics - height and lightness - cannot be compared with anything. The popularity of dormer windows is understandable and justified, since it is window structures that provide savings on home lighting, while at the same time giving the home an exclusive look, originality and charm.
The orientation of the skylights is important, in accordance with the area and climate of the area. South windows will give more sun, the north-west direction will allow you to hide the room from summer heat without creating a lack of lighting. The attic and its windows must be kept in precise proportions and combine harmoniously. All parameters and dimensions of each window must be organically combined into the overall architecturally consistent composition of the building. It’s easy to add uniqueness to a house with an attic and make it a designer’s find, thanks in no small part to attic windows and their variety.
Lucarnes and their features
Lucarnes are window openings in attic slopes and roof domes. The name is derived from the Latin word lux - light. Lucarnes have vertical frames, closed at the sides and at the top. Lucarne frames can be in plane façade walls, or they can continue these walls, or be located in parallel planes. An example of a lucarne is dormer windows in the attic.
The advantage of lucarnes over flat window structures is the additional volume for rooms, additional space attic premises With high ceilings, as well as receiving a bonus - an excellent view from the attic. The view from the skylight allows you to see not only the sky, but also the entire surrounding landscape.
The house should evoke a feeling of harmony and completeness with its appearance. The number, shape, dimensions and position of the hatches are determined based on the main parameters:
- Facade and its features, both architectural and type of decoration
- Roof view
- Roof slope
Lucarnes radically change the entire design of roof windows and are the basis for the interior design of the entire attic.
Types of lucarnes
Lucarnes with one slope
Single-pitched hatches are built into roofs that meet the condition - the slope of the slope must be at least 40 degrees. If the slope is flat, then a flat hatch with one slope will look unattractive. The flat roof of a lean-to lucarne can have a significant width. This width can even be equal to total length attic room. The advantage of this design is the absence of bevels on the attic ceiling, additional volume, excellent lighting and review. In such rooms it is possible to arrange a workplace near an illuminated hatch wall, or a place to relax.

Lucarnes with two slopes
They look great when the roof slope is more than 30 degrees. The width of hatches with two slopes has an architectural limitation - as a rule, they do not fit into more than two rafter steps. The wide gable roof hatch does not really decorate the house; the roof looks heavy and “unstable”. From the inside of the attic room, such hatches are usually covered with a flat ceiling.

Lucarnes with three slopes
Such hatches are in a special position; they look great on roofs with any slope angles and any shape. From below, these window models appear compact and not very noticeable. The most harmonious windows for any attic. The width of such hatches can be more than two meters, or three rafter intervals. The ceilings of three-pitched lucarnes are made at will and for reasons of harmony of proportions of the attic room - flat or triangular, repeating the three-pitched roof.

Low side walls at hatches
The vertical wall of the hatch can end without reaching the floor level of the attic room - up to two meters. In such cases, the roof of the hatch will have two slopes, and the window will have five corners. The shape of the ceiling in the lucarne niche will follow the contours of the roof. These types of hatches are limited in the placement of tall interior items and furniture near the window opening, due to the low walls of the hatch.
Triangular lucarnes
This type of roof window is small in size and compact, but it does not add volume to the attic. Choose a triangular lucarne in order to provide illumination to stairs, bathrooms or dressing rooms. From inside the room, triangular lucarnes have similar triangular ceilings, sharp broken lines.

Semicircular and bull's-eye windows in lucarnes
Very soft, streamlined shapes for the exterior, interesting architecture and exclusive appearance. But there are restrictions on the type of roofing coverings - only “elastic” types of tiles - bitumen, metal and ceramic tiles. The view from the street is a smooth pattern and the roof covering flows around the hatch from the top and sides, and from the inside, the ceilings in the niches of the semicircular hatches have arched, conical or cylindrical shapes.

Semi-oval windows in the form of a “bull’s eye” are decorations of the main facades of houses. Very impressive due to the softness of smooth lines on large roof slopes. The internal layout of a room with an oval or semi-oval window is preferable with one solid window, in this case there will be a lot of light, and the room will have attractive proportions.
The sizes of roof windows and hatches are determined according to the initial data:
- Sanitary standards require openings to be made in such a way that the glazed translucent surfaces make up no less than 12.5% of the floor area of the room, thereby achieving minimal insolation.
- When using opening hatch windows, the safety height requirements must be met. The lower levels of opening frames must be located no lower than 0.85 m from the floor level. If the windows are located lower than 0.85 m, then the installation of protective metal fences to the specified height is required. The fence, in addition, should be decorative and not disturb the overall appearance of the attic.
- To ensure a normal view of the surroundings and comfort for the viewer, it is necessary to maintain the dimensions of the attic windows within the level of the bottom of the glazing no higher than 1.20 m, and the top to a height exceeding 1.65 m from the floor level of the room. With a height of 1.75 m, a person has a line of sight height of about 1.65 m, and in a sitting position - 1.20 m. The height of the windows can also be determined based on the height and comfort of the residents.
Finishing the hatch from the inside is also not difficult at all - again, any available materials left after finishing attics - the same plasterboard (you can read about decorating an attic with plasterboard yourself)
The outer surface, as a rule, is also finished with the same materials that are used to decorate the main facade of the house - wood, all kinds of tiles, metal sheets, etc.
Lucarnes are rarely plastered.
The roof of the lucarne, no matter what it is made of, gable or single-pitched, also falls under general rule- the same material as the rest of the roof area, unless of course the task is to highlight it against the background of the roof.
Ventilation of hatches - how to do it correctly
Ventilation of the hatch occurs due to ventilated gaps, and its purpose is exactly the same as that of a ventilation device in the same attic - removing moisture from its structure.
There can be one or several gaps. If there are, for example, two gaps, then the first one is made between the mineral wool and the film (or continuous flooring covered with roofing felt as mentioned above). The second is done between the roof covering and the under-roofing film. This is the most successful arrangement - with it, one will dry the heat-insulating layer, the other will promote the evaporation of moisture from the bottom side.
But if the roof covering is made of flat coverings (bitumen shingles, roofing felt, sheets) then they do not leave gaps under them. They do not leave them when using film with high performance vapor permeability (at least 1000 g per m2 per day).
If the roof structure in the hatch is gable, then the air will penetrate into the holes between the counter-battens and rafters and flow upward, exiting back into the holes in the ridge.
If the hatch is single-pitched, then 2 gaps are made where the slope ends, that is, at the very ridge of the roof. With this arrangement of the hatch structure, air enters the space between the counter-battens and rafters and, passing through the ventilation gap, also exits at the very ridge of the main roof.
And if, for example, the roof surface of the hatch is located on the roof slope, then the beam (frontal) can block the ventilation. In this case, you will have to make a gap directly under the roof.
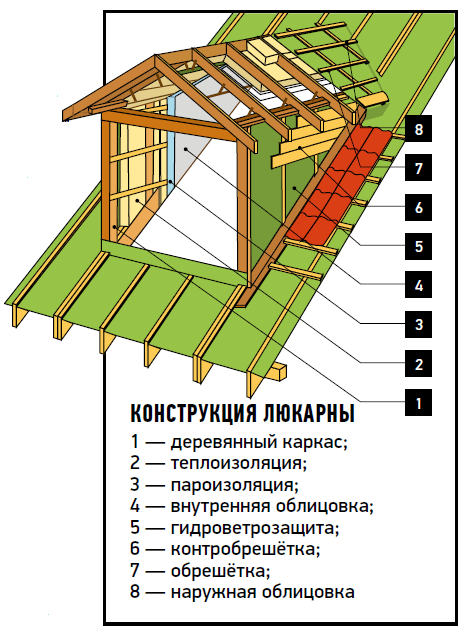
The structure and design of the hatch in the drawings
1. The design of a small hatch placed between two adjacent rafters
1. ridge beam of the main roof of the house
2. lucar roof rafters with a section of 6 x 18 cm (springs)
3. main roof rafters
4. spacer boards with a cross section of 6 x 18 cm provide rigidity
5. Mauerlat
6. racks with a cross section of 8 x 10 cm, forming the frame of the side walls of the hatch
7. wooden beam(lintel above the window)
2. Large hatch with a gable roof
1. ridge beam with a section of 6 x 10 cm for the lucarne roof
2. rafters with a section of 6 x 10 cm for the lucar roof
3. purlin with a section of 8x12 cm above the lucarne wall posts
4. Front beams. When the width of the lucarne does not exceed the triple pitch of the rafters, cut out two rafters that fall into the location of the lucarne. The shortened rafters are intercepted by two frontal beams with a section of 15 x 18 cm
5. double rafters on which the hatch structure rests. Double rafters have greater load-bearing capacity than single ones
6. main roof rafters
7. pillars with a cross section of 12×12 cm for the frame structure of the side walls of the hatch
8. wooden beam (lintel above the window)
3. Large lucarne with a pitched roof
1. the ridge beam of the roof of a house, on which the upper ends of its rafters rest
2. a purlin laid on the masonry (or ceiling). The racks of the frame of the side walls of the hatch rest on it
4. Method of laying roofing film strips
The film strips are laid horizontally, just like the rest of the roof. Place them from the bottom towards the ridge. The edges of the strips are placed one on top of the other with an overlap of 10 to 20 cm.
1. Skate not covered with film. IN gable roofs Openings are made near the skates to allow air to escape from the ventilation gaps in the slopes. The holes cannot be covered with film, so the insulation should end at a distance of 5 cm from the ridge
2. bottom strip of film, folded onto the eaves overhang
3. an additional strip of film at least 30 cm wide, ensuring the tightness of the junction of the roof slope with the roof slopes of the lucarne. Strips of film protecting roof slopes must cover this strip
4. film folded onto the side wall of the hatch; the size of its bend is 15-20 cm
5. The edge of the main roof film is bent onto the wall of the skylight to a height of 15-20 cm
6. The film on the walls of the hatch serves as a wind barrier
5. Do-it-yourself thermal insulation and finishing of the hatch
| 1. | Internal lining from plasterboard slabs |
| 2. | Mineral wool about 12 cm thick - thermal insulation of lucarne walls |
| 3. | A wooden frame mounted on the lucarne wall posts. Vapor barrier film and plasterboard slabs are attached to it |
| 4. | An additional layer of mineral wool approximately 2 cm thick, laid between the timber frame bars, to which the plasterboard slabs are attached |
| 5. | The vapor barrier film protects mineral wool from moisture, which can penetrate from the side of the heated room and reduce its thermal insulation properties. The film must be laid with joint sealing |
| 6. | Protective steel apron |
| 7. | Windproofing of lucarne walls made of roofing film |
| 8. | Wooden frame mounted on lucarne posts, boards are attached to it external cladding lucarne walls |
| 9. | Wood paneling |
| 10. | Roofing film. A film with increased vapor permeability can be laid directly on the insulation. Otherwise, there should be a ventilated gap of 2 cm wide between it and the thermal insulation. |
| 11 a. | Eaves board |
| 11 b. | Sheathing bars with a cross section of 4 x 5 cm. They carry the roof covering; laid in 30 cm increments |
| 12. | Counter battens with a cross section of 2.5 x 4 cm, nailed to the roof rafters through the roofing film |
| 13 | Thermal insulation of the lucarne roof is made of two layers of mineral wool. Its total thickness is 22-25 cm. One layer is laid between the rafters, and the second - between the frame profiles suspended ceiling. Insulation can be done with mats or mineral wool slabs. Join them very tightly so that there are no gaps between them |
| 14 | Suspensions of suspended ceiling profiles mounted on the roof rafters of the skylight |
| 15. | Suspended ceiling profiles. Vapor barrier film and plasterboards are attached to them. Distance between profiles – 40-50 cm |
Lucarna is an alternative to a roof window (or a combination of such windows), having a number of advantages and disadvantages in comparison with it. It is more interesting from an architectural point of view; moreover, a vertical window can be opened to ventilate the room at any time of the year, while snow may lie on a roof window built into the roof in winter, which does not allow it to be opened and prevents light from entering the room. At the same time, a vertical skylight window does not illuminate the room as evenly as an inclined one. attic of that the same size, since the side walls and roof of the lucarne narrow the light flux. Of course, the degree of illumination of an attic with a skylight will depend on many factors, including the size of the window, the slope of the main roof and the method of installing the slopes, but in any case there will be more darkened areas in the room than when using In addition, build a roof window into the roof much easier than lucarne. Let us note that its construction involves many structurally complex components, so the hatch should be erected on the basis of a detailed design, entrusting installation only to highly qualified specialists.
Visualization: Mavlyuda Melnikova/Burda Media
Lucarne is a structure that should form a single whole with the roof of the building. This means that when installing a hatchway, it is necessary to hermetically connect its roof to the main roof, perform high-quality insulation and installation of vapor and waterproofing, and also, if necessary, provide for ventilation of the walls, the roof of the hatchway and additional ventilation elements for complete ventilation of the main roof structure in the area where it is interrupted by a lucar. I'll note important point: when creating a vapor barrier, all seams and joints should be glued with special materials (tapes, adhesives, pastes). Their choice depends on the type of surface to which the vapor barrier film is adjacent. In particular, the film is glued to rough substrates (for example, unplaned wood) with adhesives and pastes. The use of single- and double-sided tapes in this case is unacceptable.
Valery Nesterov
General Director of the company "Derken"
DESIGN FEATURES
In most cases, the walls of the hatch are made in the form of a frame made of wooden beams, fixed on truss structure roof of the building. The width of the hatch, as a rule, corresponds to several rafter spans, which means that its design involves a gap in the rafter system. In order for the roof to maintain the necessary load-bearing capacity, in the skylight area it is necessary to strengthen it in one way or another, the choice of which is carried out by the design organization based on information about the length of the slope, the slope of the roof, the pitch of the rafters, the load from the skylight, etc. Often additional vertical racks. If the layout of the attic does not allow the presence of such racks, then reinforced unsupported purlins are installed (for example, in the form of double rafter legs or beams made of laminated wood) and the side walls of the hatch are supported on them.
They are filled with insulation - usually slabs of stone or glass fiber, which are placed spaced between the frame elements. In places where the lucar frame joins the rafters, it is necessary to use trimmed slabs, carefully compacting them during installation. According to a number of experts, this is a problematic unit in the hatch design. Even with high-quality execution installation work gaps between the plates and wooden frame, which is fraught with freezing of the walls of the hatch in these areas. Moreover, the use of alternative materials that can create a continuous heat insulating layer (for example, sprayed polyurethane foam or blown ecowool) is not economically justified if the main roof is insulated with stone or glass fiber slabs.
When installing a skylight, it is important to consider the issue of ventilation of its roof. This is a measure to protect the fiber insulation and wooden elements structures from moisture. Air flow under the roof is usually organized through gaps in the eaves overhang and/or holes in the roof gable. To achieve effective roof ventilation, in many cases, two counter-lattice contours are installed (it is its bars that create gaps for air movement), placing them in two directions. The first contour is perpendicular, and the second is parallel to the eaves overhang. This is guaranteed to ensure the movement of air entering under the roof from both the eaves and the pediment. For the hood, you can provide - depending on the shape of the roof - a ventilated ridge or pitched ventilation elements installed in the upper part of the hatch slopes. Another option is to direct the air flow into the slope of the main roof, from where it will be removed through a ventilated ridge. For this purpose, ventilation gaps on the roof of the lucarne are combined with ventilation gaps on the roof of the house.
Mikhail Chernyshov
Head of Technical Services at Rheinzink
From the inside of the room, the fibrous insulation is covered with a vapor barrier film (fixing it with staples or nails to the rafters), on top of which the base for finishing is fixed, and then the finishing itself. The vapor barrier is laid with an overlap of at least 100 mm; the overlaps and junctions of the films are sealed with special materials (single- and double-sided tapes, adhesives, pastes). On the street side, the thermal insulation is covered with a hydro-windproof membrane (it is also fixed with staples or nails), then a counter-lattice is usually installed, and then a substructure for exterior finishing and the finishing itself. The counter grill allows for a ventilation gap of 30–50 mm. In terms of design, the roof of a lucar in most cases does not differ from the main roof of the building and also requires a layer of insulation between the rafters, vapor insulation, hydro-wind protection, a ventilation gap formed by a counter-batten, a lath (solid or stepwise), on top of which the roof is laid. Steam insulation and ventilation gaps are measures necessary to protect insulation and wooden elements from moisture due to condensation of water vapor flowing from the attic towards the street.
An important question when constructing lucarne walls: how to organize the flow and exhaust of air from the ventilation gap? One of the options is to connect the ventilation ducts in the walls of the hatch with the ventilation ducts of the slope located under it, as well as with the ventilation ducts available in the roof of the hatch. Then the air will enter under the roof at the overhang of its eaves, move through the ventilation gaps and be removed either through a ventilated ridge on the skylight roof, or - if it is unventilated - through the ridge of the main roof, to which air from the skylight roof should flow freely. (For this purpose, the lucarne roof structure provides, in particular, for breaks in the line of the counter-lattice bars so that air can freely penetrate from one rafter span to another.) Let us recall that the air flow under the lucarne is carried out through the gaps on the overhang of its eaves or holes in its pediment.
If lucarna small size, and in the attic there is no room with high humidity, then, according to some experts, it is possible to do without ventilation of its structure at all, provided high-quality insulation and creating a reliable vapor barrier. Let us also note this point: the hatch itself is an obstacle to the movement of air in the ventilation gap of the main roof, and therefore, to enhance its inflow and exhaust, additional ventilation elements are installed on the roof slope (aerators, ventilation tiles, etc.). They are placed before and after the hatchway. The more lucars there are on the roof, the more difficult it is to achieve complete ventilation of its structure. Lucaren roofs come in a variety of shapes. They are single-, gable-, gable-hip (with triangular slopes), semi-circular, with a curved surface (they are called “ bat", "bull's eye"), etc.
The walls and roof of the skylight are adjacent to the roof slope of the building, and the locations of these junctions are quite complex from the point of view of design and installation. To avoid problems during the operation of the house, we can recommend that the customer demand from the design organization a detailed drawing of the skylight structure, and also involve only professional roofing companies for its construction. Thus, it is very important to correctly complete the area where the valley formed by the lucarne slope and the eaves overhang of this slope converge. Often, unscrupulous contractors do not glue the overlaps of the waterproof and windproof film here, arrange the valley itself in violation of technology, do poor-quality lining of the eaves overhang, etc. Meanwhile, snow bags form in this area in winter, and during a thaw there is a danger of capillary penetration of moisture under the roof. Only correct and careful performance of roofing work will avoid leaks in this area.
Konstantin Simonov
General Director of the company "Skif"
Depending on the architect’s plan, the roof of the lucarne can be covered with the same roofing material as the main roof, or with a different one. At the same time, difficulties may arise when arranging the roof of the lucaren. Thus, it is often problematic to use large-format or high-profile materials - ceramic and metal tiles (regular or composite), corrugated bitumen or asbestos-cement sheets, etc. It is more convenient to use coatings laid in a folded manner (copper, zinc-titanium), as well as materials in the form of low-profile or flat tiles - ceramic or cement-sand tiles (in particular, “beaver tail”), slate, flexible tiles, piece elements made of copper or zinc-titanium (diamonds, rectangles, plates in the shape of a “beaver tail”), etc. When When installing the roof, special care should be taken to connect the roof hatch to the main roof covering.
So, if the roof of the lucarne is gable, then at the point where its slopes meet the roof of the building two valleys appear. It is important to ensure the integrity of the roof both in the valley itself and at the junction of the lower edge of the valley with the slope of the main roof, as well as in the area where the roof adjoins the walls of the skylight (using different solutions for this depending on the type of roofing material: for example, in the case of ceramic or cement-sand tiles - grooves made of painted aluminum or galvanized steel, corrugated tapes made of aluminum, lead, copper, special profile metal clamping strips, etc.). When there are several lucarnes on the roof located close to each other, large snow pockets form between them and the risk of leaks under the roof increases due to the capillary rise of melt water in the places where the lucarne adjoins the roof of the building.
Alternative to lucarnes
An alternative to skylights is skylights. They are installed on roofs with a slope from 15 to 90°. The frames and sashes of dormer windows are most often made from laminated wood. Double-glazed windows are usually single-chamber, energy-saving. For a hermetic connection of the roof window with the roof, as well as for draining rainwater, the product is equipped with a flashing (in the standard version - aluminum with polymer coating), suitable for a certain roofing material. You can install a combination of skylights on the roof.
Add-ons various shapes Flat windows above the roof or built into it are called dormer windows. In ancient times, this type of roof window became known as a lucarne, and even today many people call it that way.
Nowadays, the lucarne or dormer window is mainly considered as stylish and unusual decorative detail roofs of the house. However, many people forget that, in addition to its beauty, this roofing element performs many practical problems. In this article, “Dream House” will tell you about the history of lucarne, its varieties and characteristics.
What is lucarne and when did it appear?
A lucarney is usually called a superstructure over the slope of an attic roof with a window on the facade. This design is also called a “dormer” or roof window. Steel hatches business card architectural style, dominant at the turn of the late Gothic and early Renaissance. In this era, the attic window was only beautiful decorative element and the only way to ventilate the attic of the building.
It was not uncommon for the façade of the hatch to be decorated with rich gilding and mosaic masonry. In many European countries, distinctive house signs were installed on it. In England it is closer to XVI century The dormer window has become a mandatory component of the home of rich people. And in France, it was customary to equip castles and palaces with this roofing element.


Perhaps the skylight window would have remained only a decorative element, giving the building pretentiousness and pretentiousness, but gradually the population of Europe began to increase, which created a need for additional living space. Based on the need that arose, the authorities decided to make attic spaces residential, and the window opening in the roof became the only opportunity to illuminate and ventilate the rooms under the roof. And even in our time, attic floors are often used as living spaces, so lucarna is not only an opportunity to bring a touch of flair to your home classic styles, but also an important functional element.


The types and characteristics of lucarenes vary depending on design features, as well as window shapes. The most common classification of roof windows is:
- WITH flat roof . The slope of the roof in this case ranges from 5 to 15 degrees. The design features of the hatch with a flat roof allow maximum illumination and ventilation of the room. However, for comfortable operation such a dormer window must be equipped.
- WITH pitched roof . In this case, the roof slope is at least 15 degrees. Depending on decorative purposes, the shape of the roof can be either rectangular or trapezoidal.
- With a gable roof. A dormer window with a gable roof allows you to maximize the space of the attic floor, and therefore this type of skylight is most often installed in residential premises.
- With hip roof. This type of dormer windows is equipped with a gable roof, which allows you to maximize the size of the usable space.
- Triangular, round and semicircular windows . As a rule, windows of unusual geometric shapes are used to give the building a certain style. They fit perfectly into common roof, interestingly changing its shape.

Characteristics of lucaren
Nowadays, a roof window is most often installed either during the reconstruction of ancient buildings, or for the purpose of maximum use usable area attic floor. In the second case, when designing a skylight, it is very important to take into account the main functional tasks - the possibility of additional lighting and comfortable ventilation.
The size and shape of the dormer window is determined depending on the design features of the roof. In addition, even at the design stage, it is important to decide on the place where the hatch will be located, because its functionality largely depends on this.

For example, hatches located in the end attic walls, are highly convenient to use, but it makes no sense to consider them as a source of additional lighting.
Windows located vertically are recommended to be installed on very low roofs, when, due to the small angle of inclination, they literally hang over the house. A vertical dormer window allows you to increase the area and degree of illumination. However, design features This hatchway changes the geometry of the roof, which complicates the process of clearing snow and disrupts the air exchange in the room. To reduce these problems, it is imperative to install a drainage system along with the window. Vertical window lucarna gives the building a certain bulkiness and pomp, so most often they are erected on large country houses. But dormers of this type fit quite harmoniously into literally any architectural style.

Another type of vertical skylight are the so-called “recessed” skylights. Their difference from the previous type of dormer window is manifested only in the fact that the window leaf itself is mounted deep into the structure. “Recessed” hatches are most convenient to use in cases where it is necessary to provide access to a terrace or balcony. However, they provide virtually no additional lighting.


The most popular roof window is the inclined type. The peculiarity of this design is that the angle of the window follows the angle of the roof, due to which the illumination of the attic spaces increases by an average of 50%. Since in this case lucarne acts as component, it does not destroy the geometry of the roof and does not introduce disharmony into its shape. However, it must be taken into account that it is almost impossible to install a skylight yourself, because its installation must include waterproofing, protective procedures, and insulation. In addition, you should not place the dormer window on sunny side at home, because in this case the lighting will be too bright.


Regardless of the types and shapes, lucarne is always original decoration Houses. However, it is extremely important that this design harmoniously fits into the style and color of the roof, creating a coherent ensemble with it.
Despite the fact that skylights were invented to illuminate the attic, skylights are still designed quite often, especially in houses made in a traditional architectural style. From a design point of view, this is not the most difficult element to perform. Therefore, it makes sense to familiarize yourself with the different possible solutions.
Lucarna- This is a type of wooden roof structure in which the window is placed vertically. Depending on its width, an opening of a certain size is made in the plane of the roof slope. This, in turn, suggests various ways its implementation.
The first method is between the rafters

This is the easiest way to perform a lucarne, since you do not need to change load-bearing structure roofs. It is used in cases where the width of the hatch may be less than the distance between the rafters. This means that the window will most often occupy the entire facade surface of the hatch, and its width will not be too large - usually 60 or 90 cm. This window size usually does not provide enough light in the attic, and therefore several small hatches are often designed, located nearby.
The design of the hatch, placed between the rafters, is extremely simple, since its walls are just a few boards nailed at the top to the flanges, that is, shortened rafters (in in this case- to the beams that form the ceiling above the hatch), and below - to the roof rafters, between which, in fact, it is arranged. Boards 38 mm thick and 10 or 14 cm wide, spaced in 60 cm increments, will be sufficient, just like in frame wooden house. This structure is so light that there is often no need to use thicker or double rafters to support it.
An excellent way to ensure the rigidity of the hatch frame is to cover it on the outside with moisture-resistant plywood (at least 9 mm thick, preferably 12 mm) or OSB boards (at least 12-15 mm thick).
The second method is on reinforced rafters

A room with a hatch will be comfortable if its width is more than half the length of the wall on which it is located, since in this case it is possible to place two windows (or one large one) so that daylight penetrates almost every corner. In addition, this method of arrangement allows you to significantly increase the area in the attic, where you can stand at full height under the slopes (that is, where the height of the room is more than 190 cm). But such a large hatch width (usually exceeding 180 cm) is associated with significant changes in the roof structure due to the fact that one or two rafters will have to be cut and replaced.
It is also mandatory to strengthen the outer rafters - usually by doubling them. The design of such a hatch is similar to the previous type - the only difference is that the roof usually has two slopes, and elongated crossbars of the roof structure are often used to install a suspended ceiling. The design of the hatch can be carried out in accordance with the principles of construction frame house from boards 38 mm thick and 10, 14 cm wide, or in the traditional way, using classic joinery and carpentry joints, from beams at least 5 cm thick.
The third method on wooden walls

For hatches wider than the triple pitch of the rafters, it is imperative to carry out calculations and design a structure that strengthens the roof structure. Sometimes just replacement and strengthening is enough rafter leg, but sometimes additional racks and purlins may also be needed. Therefore, each such case must be considered individually. In the process of working on a project, the designer makes decisions about this.
The hatch design should not additionally load the roof structure, and therefore the most the best option- if it is self-supporting. Very good decision is the construction of short walls on which, at least partially, the roof of the hatch will rest. The side walls of the hatch (frame, made of 38 x 100 mm boards) and the roof structure must be separated so that the load from the roof cannot be transferred directly to the floor.
It is recommended to make the roof of the lucarne single-pitched, reaching all the way to the ridge, since with this solution it will be the easiest to implement and the most correct, from a design point of view, method. But such a solution is not always possible, since it depends on many factors: the size of the roof, the angle of inclination of the slopes, the material roofing covering, architectural style of the house, etc.
Lucarne insulation

The most important is the thermal insulation of the hatch, made of mineral wool, but you will need, among other things, steam and windproofing films. Mineral wool laid: to insulate the walls of the hatch - a layer at least 10 cm thick, for insulation of the roof - preferably more, up to 20-25 cm. Strengthen the vapor barrier! There are hatches to the structure on the inside, while at the same time highly vapor-permeable windproof insulation is provided on the outside (on plywood sheathing). Then the thermal insulation will be between them and will be reliably protected from getting wet. Various connections between insulating films and sheet metal roofing elements are carried out as on the rest of the roof. For a specialist correct installation won't be a problem. ■
