Remote antenna for GPS on Android. How to connect an external GPS antenna to your tablet
Tablets are constantly incorporating the functions of different gadgets. Navigation was no exception. Almost a few years after the appearance of the first iPad, a tablet navigator appeared with a GPS module on board. Then navigation services and specialized programs appeared.
First you need to figure out what is actually better - a tablet navigator or a navigator as a separate gadget. Here opinions are divided into two camps. Some argue that a separate device works better, is more responsive, and is faster to navigate. Fans of tablet PCs are sure that All-in-one is much more functional, because in addition to the GPS itself, the device contains other useful features and programs. It supports all video formats, there is more internal memory, and the display itself is also larger. So which is better? Navigators (separate devices) or tablets with GPS navigation? The choice remains with the consumer, but before that we compare the advantages and disadvantages in a more extensive form.
Pros of a tablet in a car
- Possibility to install a huge display up to 12 inches. Navigators use (standard) 7 inches. But size does not play the first role. The most valuable thing is permission. At great importance The latter makes video and other media content much more indicative, it is much more convenient to surf the Internet and more comfortable to play games.
- On a Tablet PC, the Internet is used not only for entertainment and work, but also directly for navigation. So, when connected to the Internet, you can use A-GPS technology, which will speed up the operation of your module. The most interesting thing is that you can see traffic jams, accidents and similar information. Moreover, the data is automatically constantly updated.
- Powerful filling. Almost any tablet beats a navigator with its technical characteristics. For example, the navigation program Navitel is very demanding. Ordinary navigators, although they cope with it, are slow. It's a tablet mediocre does this without problems, performing other functions and tasks in the background.
- Computer functions. On the tablet you can talk on Skype, play, as mentioned above, media content, and surf the Internet. Much of this is already available in navigators, but many things will never be implemented there. For example, the ability to run office applications for working with documents, install specialized programs, etc.
- Operating system. Basically, it's Android, but Apple devices and Windows gadgets also have tablet navigation. The bottom line is that the system is flexible and can be completely customized to suit you, which you cannot do with a navigator.
- Tablets always have more powerful batteries, since they are designed for battery life, while the navigator was designed to work with constant recharging, although it also has its own battery. This is especially important in extreme conditions.
Cons of a tablet in a car
- Mounting the device. All navigators come with a mount included, while for tablets you will have to buy it separately and do it yourself. It is worth noting that expensive tablets have their own original fastenings. We talk about how best to install a tablet in a car.
- Screen. Not everyone will find a large tablet display a plus. Some will find it very bulky, covering a large area of the windshield and creating the effect of a piled-up car.
- GPS modules. When developers install a GPS receiver for a tablet, they save on chips. Accordingly, it is weaker compared to GPS, a separate device. This does not apply only to the market giants - Apple and Samsung.

Tablet navigator: Video
External GPS module for tablet
So, if you decide to install a tablet on your car, you should know that not all devices are equipped with this module. What to do in this case? The easiest way then is to buy a separate external GPS module for the tablet. By the way, the latter completely replaces all the shortcomings of the built-in modules. He sees much more satellites(even indoors) and connects to them faster. But the device also has a disadvantage. It is powered by the tablet and uses Bluetooth technology, which means that two modules will be turned on in the tablet at the same time, which drains the battery quite a lot. The only good thing is that the car has no problems with recharging.
Nowadays, satellite navigation is an integral part Everyday life,GPS is built into all mobile devices. Navigators and trackers working with GPS or domestic Glonass are becoming increasingly widespread, mainly in vehicles, in cars, etc. When working with various GPS gadgets, you often have to deal with a weak GPS signal or its complete absence. Today we’ll look at how you can strengthen the GPS signal in devices that work with it.
We will mainly talk about the antenna, but not just about the antenna that you can buy in the store, but about homemade GPS antenna, which can be connected to any device that has GPS module. This antenna, or rather the way to make it, was told to us by regular blog reader Yuri from Tambov, he, in turn, dug up this circuit on some American forum, for which many thanks to him.
The antenna was made and tested by me, despite the fact that it turned out the second time, I fully confirm the functionality of this design. An antenna was made for the Chinese, which suffered from constant signal loss with GPS satellites. It is known that this is the main problem with cheap trackers; they have weak GPS modules, which use a patch on the body of the module itself as an antenna. Such a module will only work in the open air; if you hide the device somewhere (under the hood of a car, for example), the signal is immediately lost.

Before you start making a GPS antenna, you should make sure that you can get to the GPS module to which the antenna will be connected. In a Chinese tracker, getting to the GPS module is not difficult, everything is well understood and assembled there, the photo below shows what the GPS module of the tracker looks like. It looks, in principle, almost the same on all devices, be it a tracker or a navigator. But if in a tracker it’s easy to get to it, then in a navigator there may be problems with disassembly, since the device is more complicated. Therefore, be sure to check whether it is worth disassembling your device if you do not know exactly how to do it. In addition, it is better to connect a purchased external antenna to the device connector, if such a connector is available.

Ordinary, inexpensive GPS trackers do not have such a connector. So a homemade modification is quite justified. What is good about this antenna is that it is easy to manufacture and has miniature dimensions, it is a square of 46 by 46 mm. The antenna is made of copper wire with a cross section of 2.5 mm 2. This is a regular monolithic electrical wire, which is used in electrical wiring.
Photo of GPS antenna manufacturing

![]()
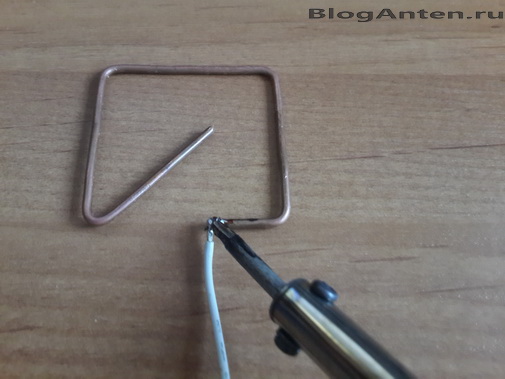
The manufacturing process of the GPS antenna is shown in detail in the photo. The point is to bend the wire correctly according to the dimensions indicated in the diagram. The wire is easily bent by hand using pliers. It is imperative to maintain all dimensions accurately; the performance of the structure depends on this.


After making the antenna itself, it will need to be soldered to the patch on the GPS module as shown in the photo. Do not under any circumstances confuse the GPS module with the GSM antenna; on the tracker the GSM antenna is displayed separately in the form of a small circuit. The GPS module is soldered into the device board. Next, the entire structure is assembled, and homemade antenna It is soldered with a small piece of wire, which is inserted into the body through a specially made hole. The antenna itself can be attached to the tracker body with regular tape.

The result of this modification became immediately noticeable; the tracker picks up satellites even indoors, whereas before it refused to do this even on a window. A stable GPS signal is now provided in almost any conditions, which is very important for a tracker. This homemade GPS antenna will fit any GPS device, the main thing is to get to the module. But the main advantage of this design is that anyone can make such a simple GPS antenna with their own hands.

Last night we put the Samsung Galaxy s1+ and my Dafi+ next to each other. Of course, no a-gps (it’s still useless in the mountains).
Dafi took a long time to calculate, about 2-3 minutes, the chip is not fast, but it saw the satellites normally and gave the coordinates to the programs.
Sams seemed to see the satellites, and in sufficient quantities, but did not give out the coordinates, although we waited for a long time. City center, Aleksandrovsky Prospekt, near Greek Square, those. There is no talk of any total shielding by high-rise buildings. As a result, in Samsa the software simply started searching for cell phone BSs.
Advantages of external GPS receiver:
1) the instinct is better (a normal external one has a decent antenna, for example, my iBlue-747 rev.B).
2) starts faster.
3) the smart battery drains less, maybe. The BT interface consumes several times less than the internal GPS.
Minus - the connection via VT is sometimes interrupted, and in some programs your track recording will be interrupted.
One problem is that until now almost all navigation programs for Android can only use the GPS receiver built into the phone. Android 2.3.x also cannot work with external receivers.
WinMobile, a mature system, had all this - already in 6 they built in a simple GPS proxy, which allowed you to connect any compatible external receiver, sit on any port and broadcast its data to 1 or several programs. And besides it there was a very functional gpsGate, which does the same thing + a bunch of additions. The programs also had a standard receiver selection option.
In Android, support for external receivers in the OS is not implemented, at least in 2.3.x, and navigation software manufacturers are simply too lazy to write something separate for this (at the same time, paid ones do not become cheaper).
Typical, from the forum “By waiting for the internal one to start working, I would have gotten there a thousand times already, and it’s a pity for the battery”
The Robot developers will understand the need for such a thing at the system level somewhere around version 4.5, apparently. And that’s not a fact.
But there are craftsmen who have written programs that replace the phone’s internal GPS with an external one. A typical navigation program does not know that it is communicating with the external, thinking that it is communicating with the internal.
Important note. It cannot be guaranteed that any of these programs will work correctly on all versions of Android and with all navigation programs.
Check. (I now have an improved (by craftsmen) firmware from Motorola based on Android 2.3.4)
For both programs to work, you need to enable the developers option "enable mock locations" .
Note. In most combinations of a proxy emulator and a navigation program in the actual navigation program you won't see satellites.
The program works correctly, sends coordinates to 2 programs at the same time, but some programs receive the signal, and at the same time display that gps is disabled (in general, true for the system chip), if I did not turn on the system gps.
Or you can turn on the system one - it will replace it.
Shows (concisely and clearly) satellites and data from the receiver.
Many options, support for various external receiver chips (including the most popular ones, SiRF III / MTK)
I like it better than 2 so far.
The program works correctly, gives coordinates to 2 programs at the same time, but you need to turn on Gps in the system options - otherwise it won’t work.
Only hard replacement of the system GPS works.
There are options for siRF III.
The program is updated periodically.
Quite suitable, but 1st is better.

All modern tablets and smartphones have built-in GPS, but they cannot be compared with full-fledged navigators. Gadgets cannot always pick up satellites in difficult reception conditions. This happens under different conditions:
- The windows in the car are covered with a special coating, which impairs signal reception.
- The tablet cannot be placed under the windshield.
- Limited visibility – this applies to special equipment.
But there is a simple way to bring your tablet as close as possible to a full-fledged navigator - install an external GPS antenna. Some motorists turn to service centers, but why pay if you can do the work yourself.
Reference! The external antenna is housed in a compact box, the size of which usually does not exceed half matchbox. A shielded cable comes out of the box; its length depends on the model, but usually the cable is 3-3.5 meters. A special connector located at the end of the cable is connected to the signal receivers, in our case, to the tablet. The antenna can also be connected to a smartphone or computer.
Installation process
When choosing an antenna, you need to explain to the seller what device the GPS signal amplifier will be used for. Modern models can be connected not only via USB, but also via Bluetooth. And now to the connection:
- The ideal solution for your smartphone would be a GPS antenna that connects to the device via Bluetooth. All data will be transmitted via the protocol. The advantage is that you won't need any additional connectors or modification.
- Due to the fact that the tablet already has a navigation application, you do not have to make new settings.
- Also, an external receiver may have a USB/PS2 connector. This interface is usually used on personal computers and laptops, but there are exceptions. As in the first case, you only need to connect the antenna to the device.
It is rare, but there are tablet models that do not have a USB input. In this case, it is worth purchasing an external Bluetooth GPS antenna. The increased efficiency of such an antenna can be explained by the presence of an autonomous power source. It is also important to secure it correctly. Some motorists take it to the roof, others attach the modifier under the glass. In any case, with an external GPS antenna, your tablet will work no worse than a separate navigator for a car.
