Connecting a GPS receiver to a laptop. What is a laptop GPS receiver?
Today, GPS navigation has become commonplace. So you won’t surprise anyone with it. Naturally, there are a lot of devices on sale in the form of mobile GPS navigators installed in the car. But some users are not satisfied with them. Drivers decide to use their own laptop as a navigator. Well, that's a good idea. But there are several important points, which are worth paying attention to.
GPS Navigation Basics
Before talking about what a laptop navigator is, you should take a short excursion into the history of the creation of the global positioning system (GPS). The corresponding idea appeared back in the 60s. last century. It was implemented 20 years later. Now, speaking about GPS and without going into technical details, it can be noted that the entire system is built on three main components. These are space satellites, ground-based receiving and transmitting stations and the navigators themselves.
The satellites revolve around the Earth in circular orbits (20,200 km) with a periodicity of 11 hours 58 minutes, completing a full circle per sidereal day (23 hours 56 minutes). GPS navigation, roughly speaking, is based on measuring the difference in the time of signal transmission and reception. In this way, the distance between several points is determined. The satellites rotate in six planes (four satellites in each). There are 32 modules in one segment. This allows high accuracy determine the location of any moving transceiver device.
Using maps
With development computer technology Electronic cards have appeared in the world. Of course, a laptop navigator can use them, but there is one small problem. The fact is that without a GPS connection, it will be simply impossible to track your current location either on the navigator itself or on the laptop. Such maps are only suitable for estimating the desired route of movement, nothing more.

It goes without saying that modern electronic maps are very accurate. There are even 3D models. Naturally, they are all updated periodically. There is probably no need to explain that there can be many reasons for this, say, the construction of new residential areas, the construction of new roads, etc.
Selecting a GPS receiver
All idealists should be immediately upset. Not a single laptop navigator program will work without a means to establish a connection. In this case, there may be two main solutions. Probably, any user will object, they say, why connect a standard navigator to a laptop if you can use it standalone? Note that connecting a laptop to a global positioning system has its advantages. Agree, the laptop has a bigger screen.

The first way is to use an antenna. Its advantage is that the antenna can be moved freely. In the second case, a special device is used, similar to a regular flash drive. But both devices connect to a laptop either via Bluetooth or using a universal USB port. What exactly to choose, everyone decides for themselves. A device in the form of a flash drive for a laptop fits better in total, although in some cases there may be signal loss.
Software
Although a GPS navigator for a laptop has an accompanying software in terms of installing the same drivers or cards, however, many experts recommend using third-party software, which is universal for all types of devices connected to laptops from different manufacturers. When combined into one system, a laptop navigator can use two types of software: offline programs and applications that require the Internet or GPS.

For example, the Microsoft Auto Route app is best for exploring local attractions. There is detailed description, say, architectural monuments or museums, as well as detailed instructions for the driver. The only negative is that you will have to constantly monitor updates, because construction does not stand still. When using programs with an Internet or GPS connection, the chances of finding the shortest route and avoiding any unforeseen situations increase significantly. This is understandable, because you can control your location on the map at any given moment. Moreover, the latest information about the state of roads in terms of traffic jams, etc. is always transmitted from satellites.
Device Compatibility
In order to connect a laptop GPS navigator directly to the system, you first need to install drivers. This is done in a standard way. Either the operating system itself will detect the device and install the appropriate driver, or you will have to install it manually using the original distribution. Next, you will need to synchronize the laptop navigator with the computer system. There should be no problems using the cable and USB port. When connecting via Bluetooth, you will need to activate the connection on the laptop (it is always active on the receiver), and then proceed to search for devices. When the receiver or navigator is identified, communication is established. You can start working.

Advantages and disadvantages
There is much disagreement about the pros and cons of such integrated systems. But the most important theses are not difficult to formulate. The main advantage is that the considered system has a higher accuracy in determining the current location. But the main disadvantage is the size of the laptop. After all, it’s clear that you can’t put a laptop on the panel under the windshield - there’s not enough space. And leaving it on the seat next to you is also not an option. Well, you won’t turn your head to the right every couple of minutes!? Now it’s worth thinking about the feasibility of using such systems. At least in passenger cars It is very uncomfortable. Another thing is trucks. Truckers who drive along European routes certainly have somewhere to place such a unique GPS system.
It is a very useful and sometimes simply irreplaceable device. Using it, you can easily determine your current position and navigate your way to your destination and back. That is, this equipment allows you to turn an ordinary laptop into a full-fledged functional navigator.
What is a GPS receiver
This name refers to the system. Its operation is based on receiving signals from several satellites. Their number on average is 6. Based on the received data, the current location of the GPS receiver is calculated. This is the principle on which such a system works.
You can also find on the market GPS receiver"GLONASS". Its main difference from the previously discussed one is its nationality. That is, GPS is an American development, and GLONASS is domestic. In the technical aspect, these systems differ in that the movement of the satellites used in Russian technology, is not synchronized with the rotation of the Earth. This ensures more high level stability of readings. But, unfortunately, the service life of GLONASS satellites is much shorter.
Classification by connection method
This type of device is connected to a laptop using a cable. For this, the USB interface is used, which is found on almost all models of laptop computers. The receiver does not require additional power to operate.
Bluetooth
The external GPS module is connected to the laptop wirelessly. The distance between devices should not exceed 10 meters. The navigation equipment itself operates either from an electrical network, or from a battery, or from batteries. 
for laptop
You shouldn't buy the first gadget you come across. Correct functioning depends on several important parameters.
Firstly, you should pay attention to such an indicator as cold start time. It displays how long the equipment has been turned on after a long period of inactivity. For expensive models, this indicator may be only a couple of seconds, while for budget options its value can reach several minutes.
Secondly, great value has the sensitivity of the receiver. If the value of this parameter is low, the device may stop receiving a signal even due to changing weather conditions or when landing in vehicle. The optimal figure is 150 dbm.

How to use
The first step is to install software for working with navigation equipment. Usually it comes complete with the device itself. If it is not there, then you can download third-party software.
Once the drivers are installed, you can launch the navigation software. Applications that come with the device usually recognize GPS equipment themselves. But sometimes this doesn't happen. This can also happen when using third-party software. In this case, you must manually specify your laptop GPS receiver in the application settings.
So, the purpose of crossing an external GPS device with a laptop is to get our location in the program on the laptop (PC) in real time + track recording + monitoring of movement via the Internet.
What we have:
1) Communicator with GPS- we use it as a GPS receiver. Theoretically, any GPS device can be used.
2) Laptop with installed:
- ActiveSync (a program for connecting a PDA with a PC);
- GPSGate client;
- SASPlanet (similar to Google "Planet Earth");
- Any PC navigation program is possible, for example Ozi.
3) 3g modem- if we want to send our coordinates to the server (can be configured on the Communicator, then a 3g modem is not needed).
So, let's begin.
In the program settings:
Input: COM2 (or your hardware GPS receiver port);
Output: ActiveSync; (GPS receiver)
If there is a need to use the device as a GPS tracker, then we also add GpsGate.com (Send)(same procedure as in the mentioned post).
2) Install the GPSGate program for PC (registering...).
It is completely similar to the program for PDAs.
Here in the settings we select:
Input: ActiveSync (since our GPS signal source will be ActiveSync);
If a Navigator connected to a laptop is used as a GPS signal source, then it must be detected by the system as a device connected to some COM port (i.e., in Input we indicate the corresponding COM port).
Output: Virtual COM Port (The receiver of the GPS signal will be a virtual port, e.g. COM-6)
3) Setting up the navigation program:
Open SASPlanet - Settings - Program settings - GPS
We indicate our COM port Virtual COM Port
COM-6.
OK.

SASPlanet has a large number of maps (Yandex, Navitel, Google, etc.)
In the settings in the Source, it is better to specify “Internet + Cache”, then already viewed maps will be loaded from the Cache (from the laptop’s memory), and new ones from the Internet.
Therefore, it is logical, to save traffic, to view (open) as much as possible in advance larger plot which you plan to visit.
For example, in my spare time I look through my city and surrounding area on Navitel maps and Yandex maps, so that during city games I don’t waste time and 3G modem traffic on opening the map.
I think it’s not difficult to figure out the settings of the SASPlanet program.
4) If you want to set up GPS monitoring (tracking) using a 3g modem, then in the GPSGate settings on your laptop, select Output: GpsGate.com (Send)
In this case, the coordinates will be sent to the server not from the communicator, but from a 3G modem or other Internet connection on your laptop.
P.S. Today we are playing again, so I will test this combination in field conditions. I'll take screenshots and post the results.
I attach the PDA to the windshield on the right, and I attach the 3-g modem to the front console under the windshield.
The navigator guides big map in real time.
The headquarters can track our location in real time from the website gpsgate.com, because... parallel coordinates are sent there.
-===============-
Here is the test result.
In the screenshot green depicts the trek (path) we made throughout the night. Sometimes, in places where the cellular connection was interrupted or was unstable, the coordinates were not transferred to the server, so the map has some jumps in the track from the road.
In general, sending coordinates to the server was successful; the headquarters from home could also observe my crew in real time on the map.
At the same time, SASPlanet with Yandex maps was opened on the laptop, on which we could also see our location and plan our further route.
Many travel enthusiasts have long begun to use GPS devices when spending their leisure time.
Someone uses navigators to move from one settlement in another along the nearest highway/road, using, as a rule, navigation programs with vector maps. And some prefer a more extreme pastime, getting from point A to point B along the nearest route in SUVs. For the latter, vector maps are not so important; the main thing here is to know the terrain features of the nearest area, and navigation programs with raster maps linked to coordinates are used.
I set out to connect an external GPS receiver to a laptop on which I can install various programs for working with vector and raster maps in order to get handy tool planning a route and viewing your current location. At the same time, I wanted to transfer GPS data to the server so that my location could be tracked remotely (improvised GPS tracker).
So, if you are interested in this topic, welcome to the topic.
What do we have?:
- Communicator with GPS
- Laptop
- 3g modem (can be excluded)
The laptop must have certain software installed:
- To synchronize PDA with PC (in my case, “ActiveSync” - for Windows XP, or “Windows Mobile Device Center” - for Windows 7, Vista);
- Navigation programs. For example, OziExplorer (for raster maps), SASPlanet;
- A program for processing a GPS signal from a receiver.
1) GPSGate.
First, we will achieve the transmission of a GPS signal from an external device to a laptop.
Here the scheme will be simple:
- The GPS signal is supplied to the PDA through the hardware port COM2 (in my case);
- The PDA is synchronized with the laptop using ActiveSync;
- Using the GPSGate application installed on the PDA, the GPS signal is redirected from COM2 to the ActiveSync port;
- The GPSGate program installed on the laptop receives the signal from the ActiveSync port and redirects it to the virtual COM port (in my case COM6);
- In the navigation program installed on the laptop, we specify our virtual port created in GPSGate as the source of the GPS signal.
Now let's move from theory to practice.
Setting up a GSP receiver
Setting up the program:
- In the "tab" Input" indicates the hardware port of your GPS receiver. On a PDA, this is usually the COM2 port. You can check by going to Control panel - External GPS- Equipment .
- On the "tab" Output" indicates the recipients of the GPS signal.
Here, from the drop-down list, select " ActiveSync"so that the received GPS signal is redirected to the connection port of the PDA and laptop. - You can now select the menu " Online". The icons should be green. (included), which means that there is currently a connection with satellites.
Now we have achieved the transmission of a GPS signal from the PDA to the laptop.
Here you can duplicate the transmission of a GPS signal to the GPSGate server to monitor your position (pre-registration on the website is required).
To do this, you need to go to the " Output"add item" gpsgate.com (Send)"and in the settings for connecting to the server, specify your login/password on the website gpsgate.com. Data transfer from the PDA to the server will be carried out via cellular communications. If you have a 3G modem, you can make similar settings in the program
GPSGate installed on a laptop. 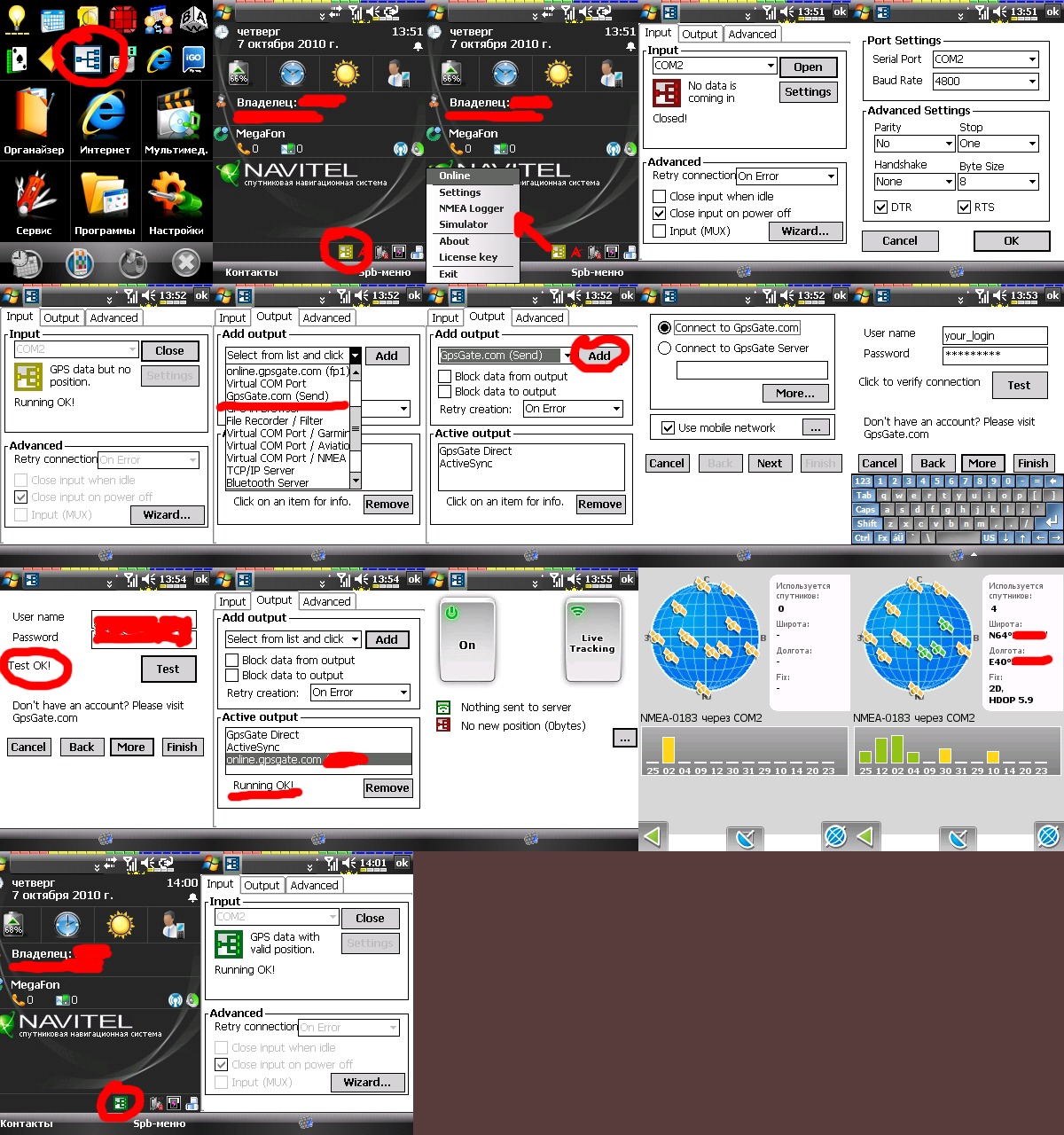
Let's move on to setting up the laptop
It is assumed that ActiveSync, GPSGate and SASPlanet (or Google Earth) are already installed here.
- In GPSGate settings select " Input" - ActiveSync (since our GPS signal source will be ActiveSync);
- IN " Output“we choose Virtual COM Port(The receiver of the GPS signal will be a virtual port, e.g. COM-6);
- In the program settings SASPlanet: Options - Program settings - GPS
We specify our Virtual COM-Port in the COM port COM-6.


This completes the basic program settings.
SASPlanet has a large number of maps (Yandex, Navitel, Google, etc.)
In settings in Source it's better to indicate " Internet + Cache“, then already viewed maps will be loaded from the Cache (from the laptop’s memory), and new ones from the Internet.
Therefore, it would be more logical, to save traffic, to preview as much of the area as possible that you plan to visit on your trip.
What's the result?
We receive a GPS signal on external device and transfer it to the laptop, where the GPS data is processed and we receive our current location linked to a raster or vector map in the SASPlanet program (any other similar one).
In parallel with this, data about our movement and current location are sent to the server. That. You can remotely view our location and route for a specified period of time.
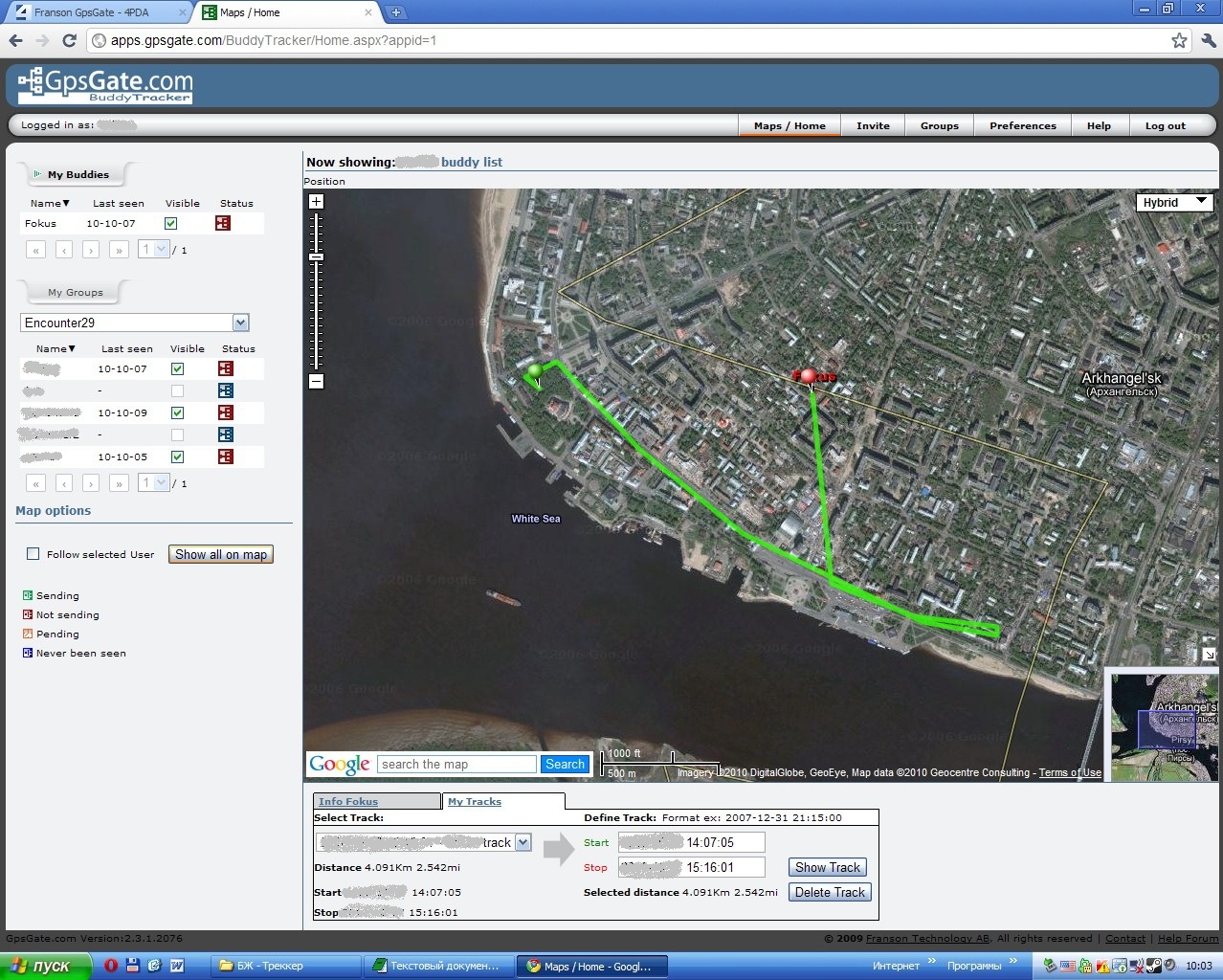
For what?
I use this during team active city games:
1) The headquarters remotely controls and coordinates the simultaneous movement of all crews of the team.
2) Navigation programs on a laptop have greater functionality and clarity than in portable GPS devices. You can quickly plan and coordinate your route and choose the most suitable one from a variety of maps.
Many off-road travelers connect their GPS devices to smaller netbooks and use the OziExplorer program with raster topographic maps, which usually have more information about the terrain.
Fans of classic tourism will also find it more interesting to watch their movements around the great interactive map, where you can see nearby attractions displayed on a Google map.
